We don’t suppose twice about utilizing our arms all through the day for duties that also thwart refined robots—pouring espresso with out spilling when half-awake, folding laundry with out ripping delicate materials.
The complexity of our arms is partly to thank. They’re wonders of organic engineering: Arduous skeleton retains their form and integrity and lets fingers bear weight. Delicate tissues, corresponding to muscle tissue and ligaments, give them dexterity. Because of evolution, all these “biomaterials” self-assemble.
Recreating them artificially is one other matter.
Scientists have tried to make use of additive manufacturing—higher referred to as 3D printing—to recreate complicated buildings from arms to hearts. However the know-how stumbles when integrating a number of supplies into one printing course of. 3D printing a robotic hand, for instance, requires a number of printers—one to make the skeleton, one other for gentle tissue supplies—and the meeting of elements. These a number of steps improve manufacturing time and complexity.
Scientists have lengthy sought to mix completely different supplies right into a single 3D printing course of. A workforce from the gentle robotics lab at ETH Zurich has discovered a method.
The workforce geared up a 3D inkjet printer—which is predicated on the identical know-how in regular workplace printers—with machine imaginative and prescient, permitting it to quickly adapt to completely different supplies. The strategy, known as vision-controlled jetting, repeatedly gathers details about a construction’s form throughout printing to fine-tune the way it prints the subsequent layer, no matter the kind of materials.
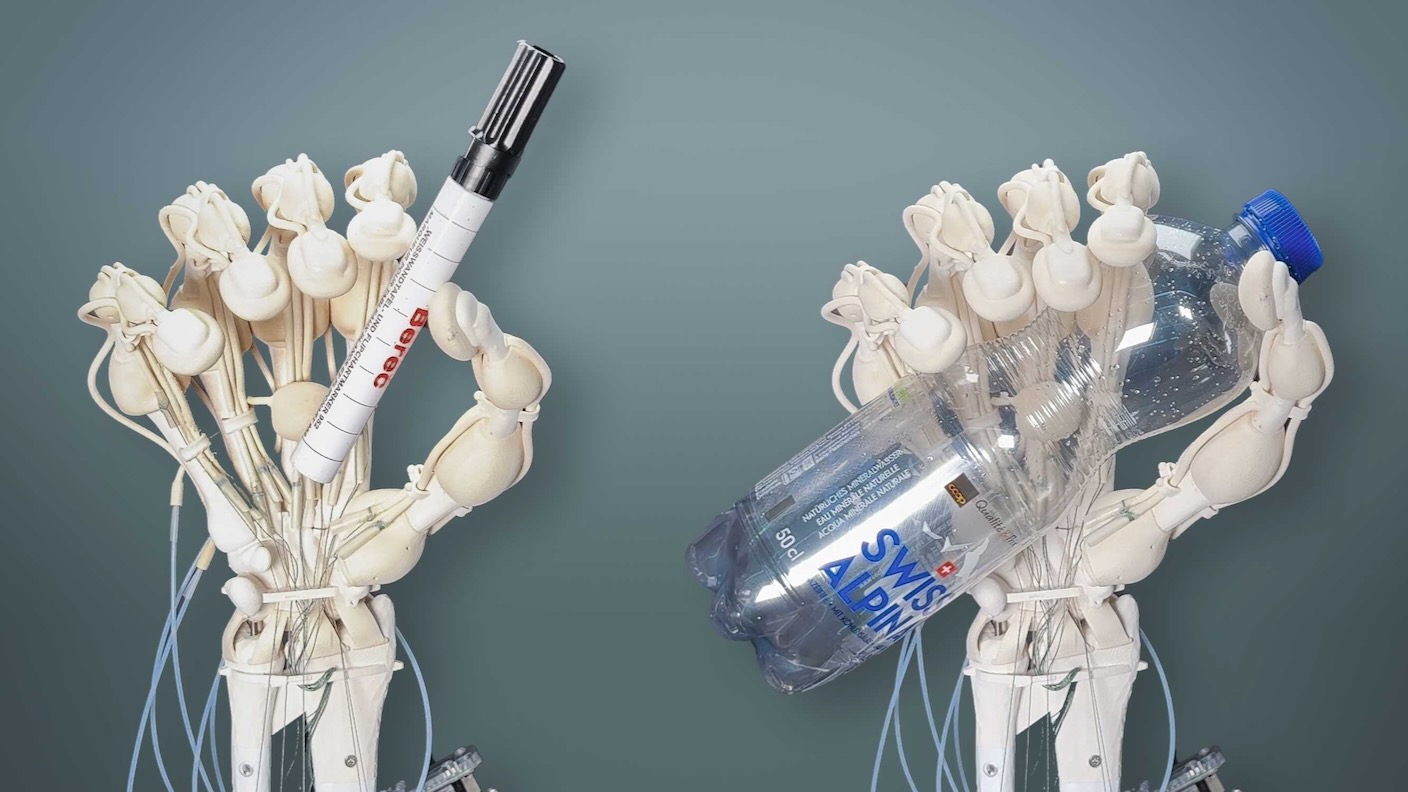
In a take a look at, the workforce 3D printed an artificial hand in a single go. Full with skeleton, ligaments, and tendons, the hand can grasp completely different objects when it “feels” stress at its fingertips.
In addition they 3D printed a construction like a human coronary heart, full with chambers, one-way valves, and the power to pump fluid at a price roughly 40 % of an grownup human’s coronary heart.
The research is “very spectacular,” Dr. Yong Lin Kong on the College of Utah, who was not concerned within the work however wrote an accompanying commentary, instructed Nature. 3D inkjet printing is already a mature know-how, he added, however this research reveals machine imaginative and prescient makes it doable to increase the know-how’s capabilities to extra complicated buildings and a number of supplies.
The Drawback With 3D Inkjet Printing
Recreating a construction utilizing typical strategies is tedious and error-prone. Engineers solid a mould to kind the specified form—say, the skeleton of a hand—then mix the preliminary construction with different supplies.
It’s a mind-numbing course of requiring cautious calibration. Like putting in a cupboard door, any errors go away it lopsided. For one thing as complicated as a robotic hand, the outcomes may be fairly Frankenstein.
Conventional strategies additionally make it tough to include supplies with completely different properties, they usually are inclined to lack the effective particulars required in one thing as complicated as an artificial hand. All these limitations kneecap what a robotic hand—and different useful buildings—can do.
Then 3D inkjet printing got here alongside. Widespread variations of those printers squeeze a liquid resin materials via lots of of hundreds of individually managed nozzles—like an workplace printer printing a photograph at excessive decision. As soon as a layer is printed, a UV gentle “units” the resin, turning it from liquid to stable. Then the printer will get to work on the subsequent layer. On this method, the printer builds a 3D object, layer by layer, on the microscopic degree.
Though extremely fast and exact, the know-how has its issues. It isn’t nice at binding completely different supplies collectively, as an example. To 3D print a useful robotic, engineers should both print elements with a number of printers after which assemble them after, or they will print an preliminary construction, solid across the half, and add further forms of supplies with desired properties.
One major disadvantage is the thickness of every layer isn’t all the time the identical. Variations within the velocity of “ink,” interference between nozzles, and shrinkage through the “setting” course of can all trigger tiny variations. However these inconsistencies add up with extra layers, leading to malfunctioning objects and printing failure.
Engineers sort out this drawback by including a blade or curler. Like flattening newly laid concrete throughout roadwork, this step ranges every layer earlier than the subsequent one begins. The answer, sadly, comes with different complications. As a result of the rollers are solely appropriate with some supplies—others gunk up the scraper—they restrict the vary of supplies that can be utilized.
What if we don’t want this step in any respect?
Eyes on the Prize
The workforce’s resolution is machine imaginative and prescient. Reasonably than scraping away further materials, scanning every layer because it’s printing helps the system detect and compensate for small errors in actual time.
The machine imaginative and prescient system makes use of 4 cameras and two lasers to scan your entire printing floor at microscopic decision.
This course of helps the printer self-correct, defined the workforce. By understanding the place there’s an excessive amount of or too little materials, the printer can change the quantity of ink deposited within the subsequent layer, basically filling earlier “potholes.” The result’s a robust 3D printing system wherein further materials doesn’t should be scraped off.
This isn’t the primary time machine imaginative and prescient has been utilized in 3D printers. However the brand new system can scan 660 occasions quicker than older ones, and it will probably analyze the rising construction’s bodily form in lower than a second, wrote Kong. This permits the 3D printer to entry a a lot bigger library of supplies, together with substances that help complicated buildings throughout printing however are eliminated later.
Translation? The system can print a brand new era of bio-inspired robots far quicker than any earlier applied sciences.
As a take a look at, the workforce printed an artificial hand with two forms of supplies: a inflexible, load-bearing materials to behave as a skeleton and a gentle bendable materials to make tendons and ligaments. They printed channels all through the hand to regulate its motion with air stress and on the similar time built-in a membrane to sense contact—basically, the fingertips.
They hooked the hand to exterior electrical elements and built-in it into somewhat strolling robotic. Because of its pressure-sensing fingertips, it might choose up completely different objects—a pen or an empty plastic water bottle.
The system additionally printed a human-like coronary heart construction with a number of chambers. When pressurizing the artificial coronary heart, it pumped fluids like its organic counterpart.
All the pieces was printed in a single go.
Subsequent Steps
The outcomes are fascinating as a result of they really feel like a breakthrough for a know-how that’s already in a mature state, Kong stated. Though commercially accessible for many years, simply by including machine imaginative and prescient provides the know-how new life.
“Excitingly, these various examples had been printed utilizing just some supplies,” he added. The workforce goals to increase the supplies they will print with and immediately add digital sensors for sensing and motion throughout printing. The system might additionally incorporate different fabrication strategies—for instance, spraying a coat of biologically energetic molecules to the floor of the arms.
Robert Katzschmann, a professor at ETH Zurich and an writer on the brand new paper, is optimistic concerning the system’s broader use. “You may consider medical implants…[or] use this for prototyping issues in tissue engineering,” he stated. “The know-how itself will solely develop.”
Picture Credit score: ETH Zurich/Thomas Buchner