| Nov 03, 2023 |
|
|
|
(Nanowerk Information) To be able to survive, organisms should management the strain inside them, from the single-cell stage to tissues and organs. Measuring these pressures in dwelling cells and tissues in physiological circumstances is a problem.
|
|
In analysis that has its origin at UC Santa Barbara, scientists now on the Cluster of Excellence Physics of Life (PoL) on the Technical College in Dresden (TU Dresden), Germany, report within the journal Nature Communications (“In situ quantification of osmotic strain inside dwelling embryonic tissues”) a brand new approach to ‘visualize’ these pressures as organisms develop. These measurements may help perceive how cells and tissues survive below strain, and reveal how issues in regulating pressures result in illness.
|
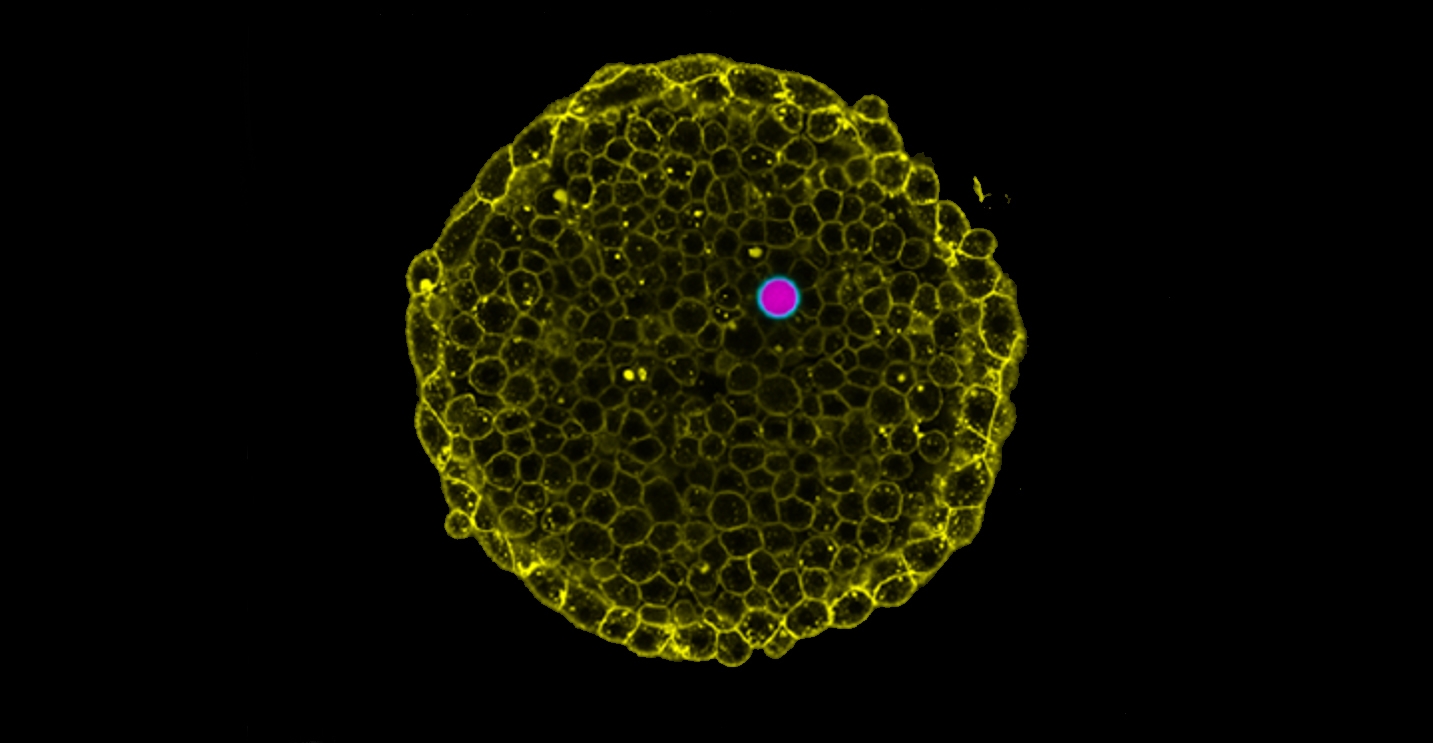 |
| Measurement of intracellular osmotic strain. (Picture: Courtesy of the researchers)
|
|
When molecules dissolved in water are separated into completely different compartments, water has the tendency to movement from one compartment to a different to equilibrate their concentrations, a course of referred to as osmosis. If some molecules can not cross the membrane that separates them, a strain imbalance — osmotic strain — builds up between compartments. This precept is the idea for a lot of technical purposes, such because the desalination of seawater or the event of moisturizing lotions. It seems that sustaining a wholesome functioning organism makes the listing, too.
|
|
Our cells are always shifting molecules out and in to forestall the strain build-up from crushing them. To take action, they use molecular pumps that enable them to maintain the strain in examine. This osmotic strain impacts many features of cells’ lives and even units their dimension.
|
|
When cells group as much as construct our tissues and organs, they, too, face a strain downside: Our vascular system, or organs such because the pancreas or liver, comprise fluid-filled cavities referred to as lumens which might be important for his or her perform. If cells fail to manage osmotic strain, these lumens might collapse or explode, with doubtlessly catastrophic penalties for the organ. To know how cells regulate strain in these tissues, or how they fail to take action in illness, it’s important to measure and ‘see’ the osmotic strain in reside tissues. However sadly, this was not attainable.
|
|
Till now.
|
|
Led by former UCSB professor Otger Campàs, who now holds the Chair of Tissue Dynamics at TU Dresden and is at present the managing director of PoL, the scientists devised a novel approach to measure the osmotic strain in dwelling cells and tissues by utilizing particular droplets referred to as double emulsions. For this strain sensor, they launched a water droplet into an oil droplet that allows water to movement by. When these “double-droplets” had been uncovered to salt options of various concentrations, water flowed out and in of the inner water droplet, altering its quantity, till pressures had been equilibrated. The researchers confirmed that the osmotic strain might be measured by merely checking the droplet dimension. They then launched these double-droplets into dwelling cells and tissues utilizing glass microcapillaries to disclose their osmotic strain.
|
|
“It seems that cells in animal tissues have the identical osmotic strain as plant cells however, in contrast to vegetation, they have to stability it always with their atmosphere to keep away from exploding, since they don’t have inflexible cell partitions,” Campàs stated.
|
|
With this easy idea, this ingenious methodology now permits scientists to “see” osmotic strain in a variety of settings. “We all know that a number of bodily processes have an effect on the working of our our bodies,” Campàs stated. “ Particularly, osmotic strain is thought to play a elementary position within the constructing of organs throughout embryogenesis, and in addition within the upkeep of wholesome grownup organs. With this new approach, we now can examine how osmotic strain impacts all these processes instantly in dwelling tissues.”
|
|
Past providing insights into the organic processes and bodily ideas that govern life, this methodology holds promising industrial and medical purposes, together with monitoring pores and skin hydration, characterization of lotions or meals, and analysis of illnesses identified to have osmotic strain imbalances, reminiscent of cardiovascular illnesses or tumors. The patent for this method is at present being issued by UC Santa Barbara, the place Campàs carried out his analysis earlier than becoming a member of TU Dresden.
|
|
Campàs’s lab beforehand developed distinctive methods to measure the tiny forces that cells create inside tissues and in addition further bodily properties utilizing minuscule single droplets. Antoine Vian, the lead writer of the work and an knowledgeable in microfluidics, the expertise that permits the era of double-emulsion droplets, emphasised their key position.
|
|
“Double-emulsions are very versatile, with many various purposes in science and expertise,” he stated. “Single droplets might be deformed, however are incompressible and don’t enable strain measurements. In distinction, double emulsion droplets can change dimension and be used as osmotic strain sensors. Their use in dwelling programs will certainly allow new and thrilling discoveries.”
|

