| Nov 03, 2023 |
|
|
|
(Nanowerk Information) Researchers led by Professor KANG Kisuk of the Heart for Nanoparticle Analysis throughout the Institute for Primary Science (IBS), have introduced a serious breakthrough within the discipline of next-generation solid-state batteries. It’s believed that their new findings will allow the creation of batteries primarily based on a novel chloride-based stable electrolyte that reveals distinctive ionic conductivity.
|
|
The findings have been revealed in Science (“Design of a trigonal halide superionic conductor by regulating cation order-disorder”).
|
Key Takeaways
|
|
The pressing want for safer battery expertise fuels analysis into non-flammable stable electrolytes, important for the way forward for solid-state batteries and electrical autos.
Improvements in chloride-based stable electrolytes, emphasizing the association of metallic ions, present promise for prime ionic conductivity and mechanical stability with out counting on expensive uncommon earth metals.
Breakthrough analysis from the IBS Heart might result in extra reasonably priced and safer vitality storage options, as demonstrated by the event of a high-performance zirconium-based solid-state battery.
|
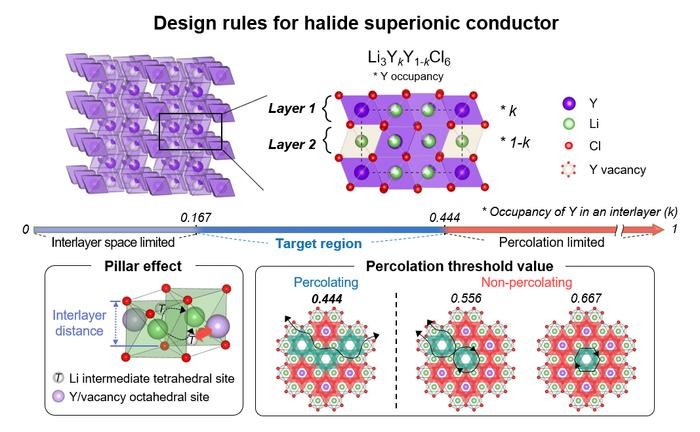 |
| The association of metallic ions (yttrium on this case) inside every layer impacts the ionic conductivity. To make sure the unobstructed motion of lithium ions, the variety of metallic ions occupying obtainable websites inside every layer ought to be lower than 0.444. Moreover, to create a sufficiently large pathway for lithium ions inside every layer, the occupancy of metallic ions ought to be greater than 0.167. Due to this fact, attaining an occupancy of metallic ions between 0.167 and 0.444 inside every layer leads to a conductive layer with excessive ionic conductivity. (Picture: IBS)
|
The Analysis
|
|
A urgent concern with present business batteries their reliance on liquid electrolytes, which ends up in flammability and explosion dangers. Due to this fact, the event of non-combustible stable electrolytes is of paramount significance for advancing solid-state battery expertise. Because the world gears as much as regulate inner combustion engine autos and increase using electrical autos within the ongoing world shift towards sustainable transportation, analysis into the core elements of secondary batteries, notably solid-state batteries, has gained vital momentum.
|
|
To make solid-state batteries sensible for on a regular basis use, it’s essential to develop supplies with excessive ionic conductivity, sturdy chemical and electrochemical stability, and mechanical flexibility. Whereas earlier analysis efficiently led to sulfide and oxide-based stable electrolytes with excessive ionic conductivity, none of those supplies totally met all these important necessities.
|
|
Up to now, scientists have additionally explored chloride-based stable electrolytes, recognized for his or her superior ionic conductivity, mechanical flexibility, and stability at excessive voltages. These properties led some to invest that chloride-based batteries are the more than likely candidates for solid-state batteries. Nevertheless, these hopes rapidly died out, because the chloride batteries have been thought of impractical because of their heavy reliance on costly uncommon earth metals, together with yttrium, scandium, and lanthanide components, as secondary elements.
|
|
To handle these issues, the IBS analysis workforce appeared on the distribution of metallic ions in chloride electrolytes. They believed the explanation trigonal chloride electrolytes can obtain low ionic conductivity is predicated on the variation of metallic ion preparations throughout the construction.
|
|
They first examined this idea on lithium yttrium chloride, a typical lithium metallic chloride compound. When the metallic ions have been positioned close to the pathway of lithium ions, electrostatic forces precipitated obstruction of their motion. Conversely, if the metallic ion occupancy was too low, the trail for lithium ions grew to become too slim, impeding their mobility.
|
|
Constructing on these insights, the analysis workforce launched methods to design electrolytes in a approach that mitigates these conflicting components, finally resulting in the profitable growth of a stable electrolyte with excessive ionic conductivity. The group went additional to efficiently exhibit this technique by making a lithium-metal-chloride solid-state battery primarily based on zirconium, which is way cheaper than the variants that make use of uncommon earth metals. This was the primary occasion the place the importance of the metallic ions association on a fabric’s ionic conductivity was demonstrated.
|
|
This analysis brings to mild the often-overlooked function of metallic ion distribution within the ionic conductivity of chloride-based stable electrolytes. It’s anticipated that the IBS Heart’s analysis will pave the best way for the event of assorted chloride-based stable electrolytes and additional drive the commercialization of solid-state batteries, promising improved affordability and security in vitality storage.
|
|
Corresponding creator KANG Kisuk states, “This newly found chloride-based stable electrolyte is poised to transcend the constraints of standard sulfide and oxide-based stable electrolytes, bringing us one step nearer to the widespread adoption of solid-state batteries.”
|

