A novel self-assembling nanosheet has the potential to considerably quicken the creation of sustainable and helpful nanomaterials for a wide range of purposes, together with vitality storage, electronics, well being, and security.
The novel self-assembling nanosheet, created by a workforce at Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory (Berkeley Lab), has the potential to considerably prolong the shelf lifetime of client merchandise. Moreover, the brand new materials’s recyclable nature might make it doable to implement a sustainable manufacturing technique that forestalls electronics and single-use packaging from ending up in landfills.
The group is the primary to successfully create a barrier materials with a number of makes use of and excellent effectivity utilizing self-assembling nanosheets. Nature revealed a report on the breakthrough on November 8th, 2023.
Our work overcomes a longstanding hurdle in nanoscience—scaling up nanomaterial synthesis into helpful supplies for manufacturing and business purposes. It’s actually thrilling as a result of this has been many years within the making.
Ting Xu, Research Lead and College Senior Scientist, Supplies Sciences Division, Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory
Utilizing nanoscience to provide useful supplies is an issue because the nanomaterial should come collectively in giant sufficient elements to be helpful. Moreover, whereas rising nanomaterials right into a product by stacking nanosheets is without doubt one of the best strategies, working with pre-existing nanosheets or nanoplatelets would inevitably lead to “stacking defects,” or areas between the nanosheets.
For those who visualize constructing a 3D construction from skinny, flat tiles, you’ll have layers up the peak of the construction, however you’ll even have gaps all through every layer wherever two tiles meet. It’s tempting to scale back the variety of gaps by making the tiles larger, however they turn out to be more durable to work with.
Emma Vargo, Research First Creator and Postdoctoral Scholar, Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory
By eschewing the serial stacked sheet approach fully, the novel nanosheet materials solves the stacking defect downside. Quite, the group mixed alternating layers of the constituent parts suspended in a solvent with mixtures of compounds identified to self-assemble into small particles.
The researchers used difficult blends of small molecules, block copolymer-based supramolecules, and nanoparticles—all of that are commercially obtainable—to construct the system.
Experiments on the Spallation Neutron Supply at Oak Ridge Nationwide Laboratory aided the researchers in understanding the early, coarse levels of the blends’ self-assembly. Because the solvent evaporates, the small particles consolidate and spontaneously manage, forming coarsely templating layers earlier than solidifying into thick nanosheets.
As a substitute of being piled one after the other in a serial course of, the ordered layers kind concurrently. The small items solely want to maneuver a brief distance to get organized and shut gaps, avoiding the problems related to transferring bigger “tiles” and the unavoidable gaps between them.
Combining nanocomposite blends with a number of “constructing blocks” of various sizes and chemistries, resembling complicated polymers and nanoparticles, wouldn’t solely deal with impurities but additionally unlock a system’s entropy, or the inherent dysfunction in mixtures of supplies that Xu’s group used to distribute the fabric’s constructing blocks. This information got here from a earlier research led by Xu.
This earlier work is expanded upon on this new research. The researchers anticipated two good traits of the difficult combine utilized on this research: Aside from possessing a excessive entropy to facilitate the self-assembly of tons of of nanosheets produced concurrently, they anticipated that the novel nanosheet construction can be little impacted by various floor chemistries.
They reasoned that this could allow the identical combination to create a barrier of safety over a spread of surfaces, resembling polyester masks or the glass display of digital gadgets.
Ease of Self-Meeting and Excessive Efficiency
The researchers collaborated with among the prime analysis facilities within the nation to evaluate the fabric’s effectiveness as a barrier coating in a wide range of purposes.
The researchers measured the mobilities of every element and the way in which it travels to kind a functioning materials by mapping out how every element joins collectively throughout assessments on the Superior Photon Supply at Argonne Nationwide Laboratory.
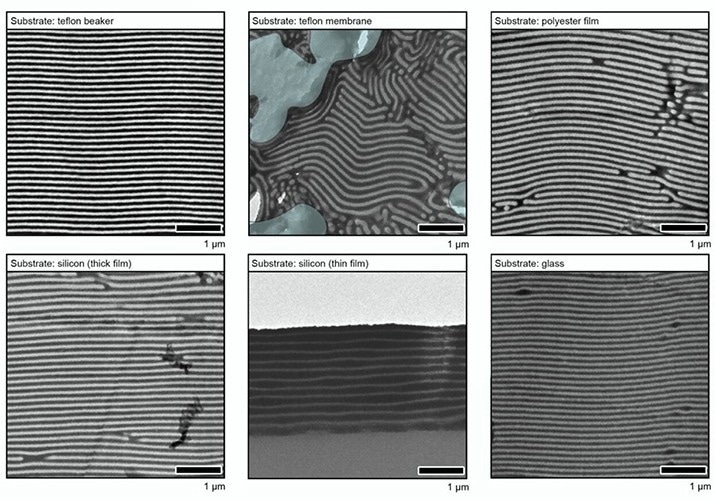
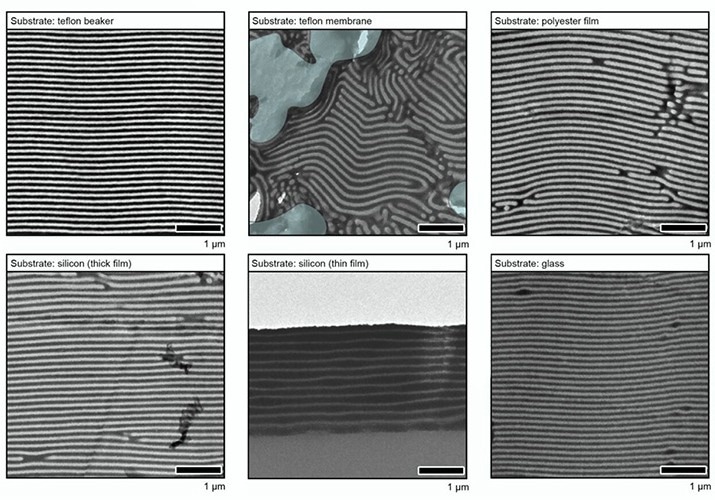
By making use of a diluted answer of polymers, natural small molecules, and nanoparticles to a wide range of substrates, together with a Teflon beaker and membrane, polyester movie, thick and skinny silicon movies, glass, and even a prototype microelectronic gadget, after which regulating the speed of movie formation, the researchers created barrier coatings based mostly on these quantitative research.
At Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Foundry, transmission electron microscopy experiments reveal that by the point the solvent evaporated, over 200 stacked nanosheets had self-assembled right into a extremely organized layered construction with a really low defect density on the substrates.
Moreover, every nanosheet was made by the researchers to be 100 nanometers thick with a number of holes and gaps. In keeping with Vargo, this makes the fabric particularly efficient in blocking the passage of electrons, water vapor, and unstable natural molecules.
The fabric has plenty of potential as a dielectric, an insulating “electron barrier” materials continuously employed in capacitors for vitality storage and laptop purposes, based on extra assessments performed on the Molecular Foundry.
Xu and colleagues, working with researchers in Berkeley Lab’s Power Applied sciences Space, confirmed that the fabric is extraordinarily efficient at filtering out unstable natural compounds that may decrease indoor air high quality when it’s utilized to porous Teflon membranes, a cloth generally used to make protecting face masks.
Moreover, the fabric will be dissolved and recast to create a brand new barrier coating, as demonstrated by the researchers in a remaining experiment performed on the Xu lab.
After proving {that a} single nanomaterial can be utilized to create a various useful materials for a spread of business purposes, the researchers now wish to enhance the fabric’s recyclability and add coloration tunability (it’s now obtainable in blue).
The opposite authors of the research are Hugo Destaillats, Ivan Kuzmenko, Jan Ilavsky, Wei-Ren Chen, William Heller, Robert O. Ritchie, Yi Liu, Le Ma, He Li, Qingteng Zhang, Junpyo Kwon, Katherine M. Evans, Xiaochen Tang, Victoria L. Tovmasyan, Jasmine Jan, and Ana C. Arias.
The Laboratory Directed Analysis and Improvement (LDRD) program at Berkeley Lab and the DOE’s Workplace of Science offered funding for the research. The Nationwide Science Basis, the Protection Menace Discount Company, and the Division of Protection contributed extra funds.
Journal Reference:
Vargo, E., et al. (2023) Practical composites by programming entropy-driven nanosheet progress. Nature. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06660-x
Supply: https://www.lbl.gov/