| Nov 10, 2023 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) RIKEN researchers have introduced low-energy units primarily based on spintronics one step nearer, by measuring the dynamics of tiny magnetic vortices (Nature Physics, “Uneven gradual dynamics of the skyrmion lattice in MnSi”).
|
Key Takeaways
|
|
RIKEN researchers have superior spintronics know-how by learning the dynamics of magnetic vortices, providing potential for extra environment friendly low-energy units.
The research focuses on nanoscale magnetic whirlpools, often called skyrmions, which require much less power to manage, promising developments in information storage and ICT.
Experiments on the Institut-Laue-Langevin, utilizing the IN15 neutron spin echo spectrometer, have been key to observing skyrmion habits in manganese monosilicide.
Findings verify theoretical predictions about skyrmions, probably paving the way in which for his or her sensible utility in info applied sciences.
The analysis crew plans additional investigation into the technology and coexistence of magnetic skyrmions, regardless of challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
|
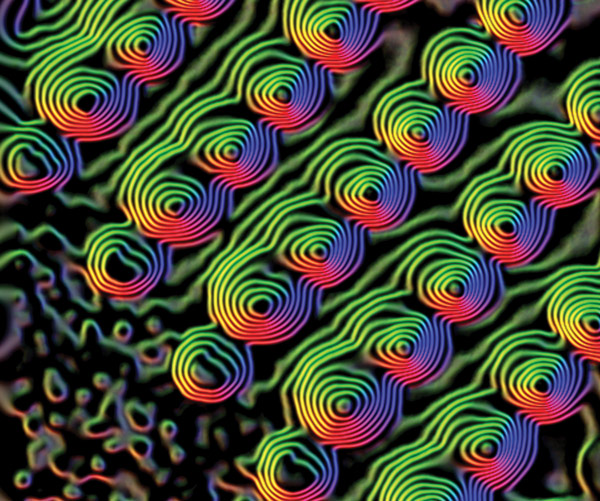 |
| Spintronic supplies that give rise to helical patterns of magnetic flux are promising for realizing units with ultralow power consumptions. (Picture: Brookhaven Nationwide Laboratory / Science photograph library)
|
The Analysis
|
|
At current, all our info applied sciences are primarily based on typical electronics, which includes shunting electrical cost round circuits. Nevertheless, electrons have one other property often called spin, which may very well be exploited to make quicker and extra environment friendly units.
|
|
Hazuki Kawano-Furukawa of the RIKEN Heart for Emergent Matter Science and her co-workers are main efforts to develop this discipline of spintronics. Specifically, they’re exploring using nanoscale magnetic whirlpools known as skyrmions.
|
|
“Skyrmions might be managed with considerably smaller currents or electrical fields,” explains Kawano-Furukawa. “This makes them extremely promising for future functions in info and communication applied sciences, similar to pc reminiscence that doesn’t want energy to maintain saved information.”
|
|
The crew centered on the fabric manganese monosilicide—a helimagnet, so-called as a result of the spins in its molecular lattice align in helical patterns. Extraordinarily delicate gear was essential to measure the bottom power magnetic excitations within the skyrmion states.
|
|
“The one technique that fulfills each the spatial and power decision necessities for this objective is the neutron spin echo method,” says Kawano-Furukawa. “We performed experiments utilizing the state-of-the-art IN15 neutron spin echo spectrometer on the Institut-Laue-Langevin in Grenoble, France. This instrument boasts the best efficiency on the planet for learning the dynamics of supplies in magnetic fields.”
|
|
The spin echo technique works by illuminating a pattern with a beam of neutrons, and measuring how the pattern’s magnetic fields have an effect on the spin and velocity of the neutrons.
|
|
By means of their observations, the crew verified theoretical predictions that the string-like constructions of skyrmions (Fig. 1) trigger an uneven dispersion of excitations within the lattice of manganese monosilicide. In Kawano-Furukawa’s phrases, these excitations ‘know’ if they’re touring parallel or antiparallel to the cores of the skyrmion whirlpools. This affirmation of concept opens up the way in which to raised exploit skyrmions.
|
|
The crew needed to wait two years to verify their outcomes. “We performed our preliminary experiment in October 2018,” she says. “Nevertheless, to attract remaining conclusions, we would have liked to verify that the habits was noticed solely within the skyrmion part, and never in one other magnetic construction known as the conical part. Because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the follow-up experiment was postponed to January 2021 and was carried out remotely, posing varied challenges.”
|
|
The crew now intends to conduct additional analysis on how magnetic skyrmions are generated. “We purpose to analyze the coexistence of the conical and skyrmion phases in manganese monosilicide,” says Kawano-Furukawa.
|

